Offices: Gurgaon, Jaipur, Indore, London, Dubai, Sweden
The Rise of Fog Computing

Data is often referred to as the new oil, and for good reason. Organizations are constantly generating and collecting vast amounts of data, and harnessing the power of this data has become essential for making informed decisions, optimizing operations, and delivering innovative services. To effectively leverage this data, businesses have traditionally turned to cloud computing. However, as the volume and velocity of data continue to grow, so do the challenges of latency, bandwidth, and privacy. This is where fog computing comes into play.
Fog computing, often seen as an extension of edge computing, is a paradigm that aims to address these challenges by bringing computing resources closer to the data source. In this blog, we will explore the concept of fog computing, its architecture, use cases, benefits, and its role in the ever-evolving landscape of computing.
What is Fog Computing?
Fog computing sometimes referred to as edge fog computing, is a decentralized computing infrastructure that extends cloud computing capabilities to the edge of the network. It was introduced to address the limitations of pure cloud computing, which typically relies on centralized data centers located far away from the data sources. This distance between data sources and cloud data centers can lead to latency, bandwidth constraints, and privacy concerns, especially in applications that require real-time processing and low-latency responses.
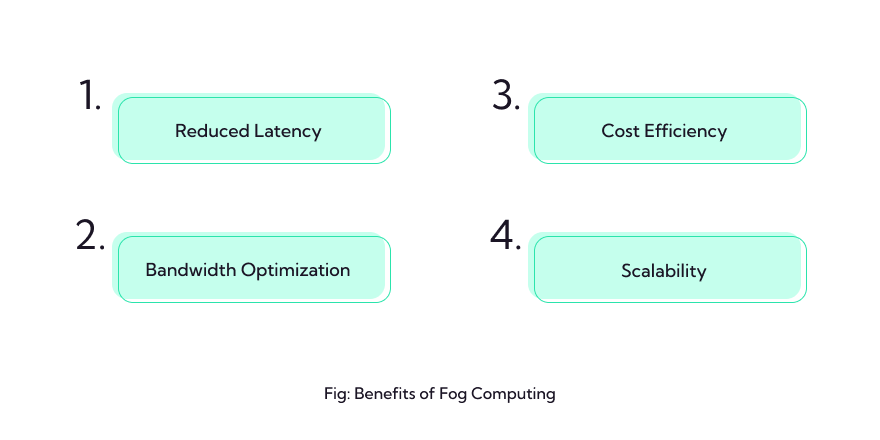
Fog computing seeks to bridge this gap by distributing computing resources closer to the data sources, essentially creating a fog-like layer of computing at the edge of the network. This proximity allows for faster data processing, reduced latency, and improved privacy, making it well-suited for a wide range of applications, from IoT (Internet of Things) devices to autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Key components of Fog computing
Edge Devices
Edge devices are the endpoints that generate or collect data. These devices can include IoT sensors, cameras, smartphones, and more. Edge devices are where data is initially produced.
Fog Nodes
Fog nodes, also known as fog servers or fog devices, act as intermediaries between edge devices and cloud data centers. These nodes are responsible for processing and storing data locally, reducing the need to send all data to the cloud for analysis.
Fog Networking
Fog computing relies on specialized networking infrastructure that supports communication between edge devices and fog nodes. This network may include technologies like 5G, Wi-Fi, and low-power, wide-area networks (LPWANs).
Cloud Data Centers
While fog computing extends computing capabilities to the edge, it doesn’t eliminate the need for cloud data centers. Cloud data centers still play a crucial role in storing and processing large volumes of data and running applications that benefit from centralized resources.
Use cases of Fog computing
IoT and Smart Devices
Fog computing is invaluable in IoT applications, where low-latency data processing is essential. For instance, in a smart home, fog nodes can process sensor data locally to control lights, thermostats, and security systems in real-time.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars require split-second decision-making based on data from sensors and cameras. Fog computing allows these vehicles to process data locally, enhancing safety and responsiveness.
Smart Cities
In smart city projects, fog computing can optimize traffic management, public safety, and utilities by processing data from various sensors and devices at the edge.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Manufacturing and industrial processes often involve sensitive and time-critical data. Fog computing can improve efficiency and safety by processing data from sensors and machines on the factory floor.
Healthcare
In healthcare, patient monitoring devices can benefit from fog computing to enable real-time monitoring and timely responses, especially in critical care scenarios.
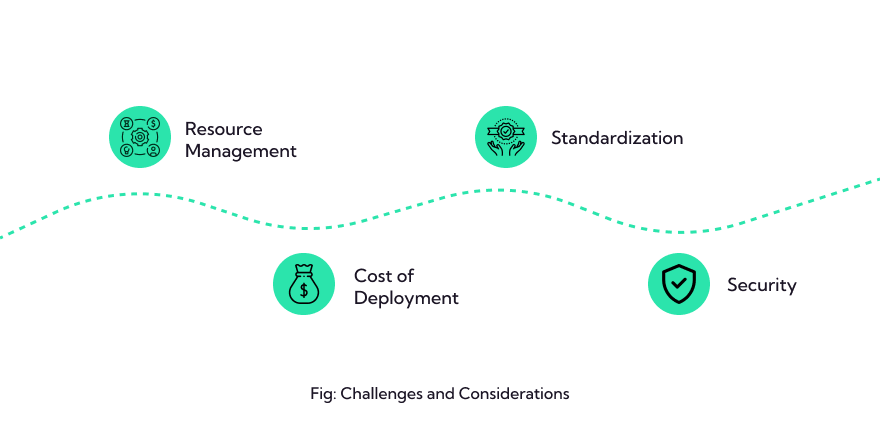
Future outlook
Fog computing is poised to play a significant role in the future of computing, especially as more devices become interconnected, and the demand for low-latency, real-time processing grows. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see greater standardization, improved security measures, and more robust fog computing architectures.
In conclusion, fog computing represents a paradigm shift in the way we process and analyze data. By bringing computing resources closer to the data source, fog computing addresses the limitations of traditional cloud computing and enables a wide range of applications that require low-latency, real-time processing. As organizations continue to explore ways to harness the power of data, fog computing is likely to become an integral part of their computing infrastructure.
Recent Posts
Wish to live a culture beyond tech ?
Quick links
Contact
-
INDIA
-
-
-
37B - Thinkvalley , Sector 32 - Gurgaon Haryana - 122002
-
J-2, Jhalana Institutional Area, Jhalana Doongri, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302004
-
Incuspaze Co-Work, 208, 2nd Floor, Apollo Premier, Vijaynagar Square, Indore (MP) 452010
Locations
-
UK
-
-
-
Wework, 33 Queen Street, London, England, EC4R 1AP
-
FZCO IFZA Business Park, Dubai Digital Park, Dubai Silicon Oasis, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
-
Herrgardsvagen 12 A 135 53 TYRESO Sweden
© All Copyright 2022 by FIFTYFIVE TECHNOLOGIES


